OmniSafe Particle Study – Single Make Up
This is the equipment and procedure used to determine the quantity and size of the particles shed into the process stream, due to galling, as a legacy metal face seal fitting is tightened.
Objectives
Compare standard metal face seal fitting with the OmniSafe torque suppression fitting over the following criteria:
- Examine the sealing surfaces of glands and gaskets with photomicrographs, for both single and multiple use makeups.
- Use a particle counter to quantify the size and number of particles produced by a single make up.
- Measure the average rotational displacement of components attached by metal face seal fittings with and without torque suppression.
- Observe the behavior of a fitting while an incremental torque is applied to an attached component.
Experiment
Pre-test SEMs – For two of each of the five sample sets pretest SEMs (scanning electron micrographs) were taken. These photomicrographs (of the sealing surfaces of glands and gaskets) were used to establish a virtual base line for evaluating the component’s post test condition.
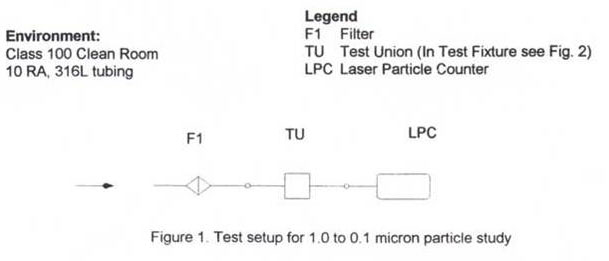
Particle measurements – This phase of the experiment measured the size and number of particles generated inside the test union as it is made up. The apparatus was set up as shown in Figure 1.
Procedure
- Make up the test union “finger tight” (i.e. maximum manual engagement of male and female nuts)
- Start the test cycle.
- Lightly tap the union until the particle counts measure zero.
- Tighten the test union 1/8 turn.
- Count particles until the reading returns to zero.
No particles are produced by the Omnisafe fitting. Legacy fittings produce particles in the 0.5 – 0.1 micron size range.
[table id=4 /]
OmniSafe vs. Standard Metal Face Fitting Glands
[tabs style=”boxed” id=”particle-study-multiple” css=”product-tabber” title=””] [tab title=”14x Magnification – Gland”]
These S.E.M.s show the galling of the crown of the torroid (red arrow) on a gland of a legacy metal face seal fitting (top view) after one mate with a nickel gasket.
The Omnisafe gland (bottom view) shows no galling after one mate with a nickel gasket. Pure compression, without rotation, does not cause galling of sealing surfaces.
[/tab] [tab title=”200x Magnification – Gland”]
Under higher magnification, these S.E.M.s show the fracture of the polished surface of the crown of the torroid on a gland of a legacy metal face seal fitting (top view). This is caused by rotational forces against the nickel gasket.
The Omnisafe gland (bottom view) shows no surface degradation after one mate with a gasket. Pure compression, of the gland into the gasket maintains the smooth, polished, corrosion resistant surfaces.
[/tab] [tab title=”1000x Magnification – Gland”]
Under the highest magnification, these S.E.M.s show the source of the 0.5 to 0.1 micron particles on a gland of a legacy metal face seal fitting (top view) after compression with rotation against a nickel gasket.
The Omnisafe gland (bottom view) shows no galling or particle generation.
[/tab] [/tabs]
OmniSafe vs. Standard Metal Face Fitting Gaskets
[tabs style=”boxed” id=”particle-study-multiple” css=”product-tabber” title=””] [tab title=”14x Magnification – Gasket”]
These S.E.M.s show the galling of the sealing area on the nickel gasket of a legacy metal face seal fitting (top view) after one mate with a SS316L gland.
The Omnisafe gasket (bottom view) shows no gasket galling after one mate with a SS316L gland. Pure compression, without rotation, does not cause galling of the softer, sacrificial, nickel surface.
[/tab] [tab title=”200x Magnification – Gasket”]
Under higher magnification, these S.E.M.s show the fractured surface of the nickel gasket of a legacy metal face seal fitting (top view) due to rotational forces against a SS316L gland.
The Omnisafe gasket (bottom view) shows no tearing of the smooth surface.
[/tab] [tab title=”1000x Magnification – Gasket”]
Under the highest magnification, these S.E.M.s show the source of the 0.5 to 0.1 micron particles from the nickel gasket of a legacy metal face seal fitting (top view) after compression with rotation against a SS316L gland. The mate and demate operations both shed particles.
The Omnisafe gasket (bottom view) shows no particle generation after one mate/demate with a SS316L gland. Pure compression, without rotation, does not lead to galling of sealing surfaces and resultant particles.
[/tab] [/tabs]